
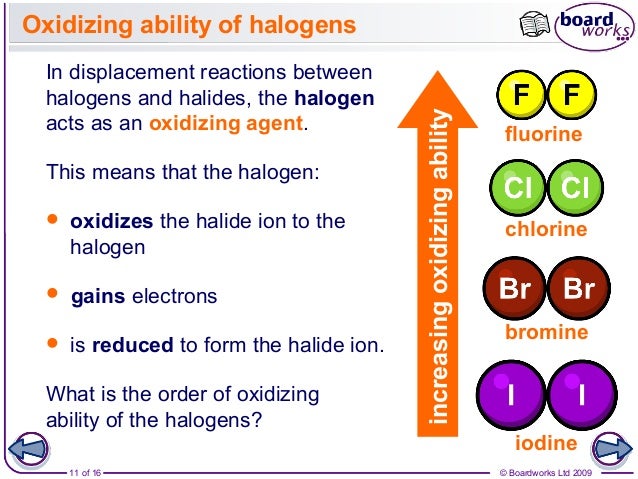
The most powerful oxidising agent in the halogen family is fluorine it also oxidises other halide ions in the solution. As a result, they have significant oxidising properties. In addition, halogens efficiently receive electrons because they lack one electron and form an octet.

Halogens are, therefore, highly reactive, so thus frequently create halides when they react with metal and non-metal.Īs we move farther from the group, the halogens’ reactivity declines. When halogens are combined with highly electronegative oxygen or fluorine atoms, they can increase oxidation. Astatine, which would be a radioactive substance, has no stable isotopes.Īs usual, halogens have a -1 oxidation state, although bromine, chlorine, and iodine have +1, +3, +5, +7 oxidation levels, respectively. It is also the rare naturally occurring substance in the Earth’s crust. At is the symbol for astatine, and its atomic number is 85.Iodine is the 53rd element of the periodic table, with the sign I.
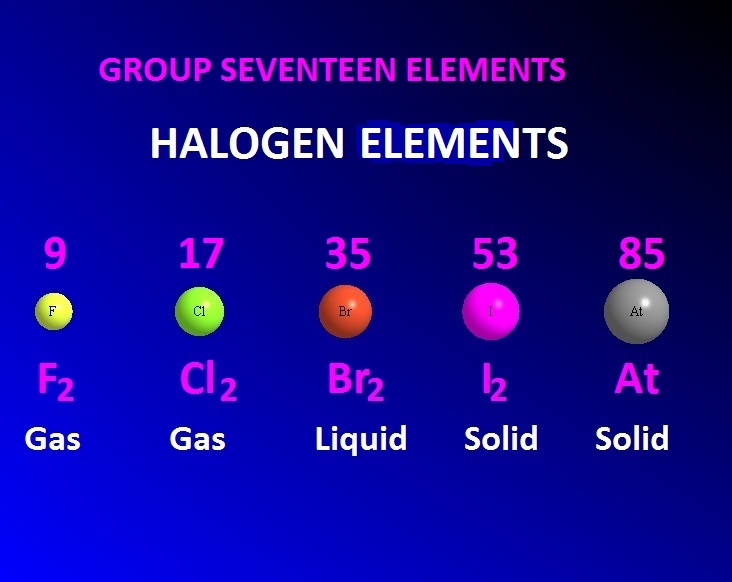
It is a liquid at ambient temperatures and pressure.

Halogens include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, as well as astatine. Halogens ListĮither there are 5 or 6 halogens, based on who we believe. The oxidation state that an element exhibit determines its reactivity and chemical characteristics. Halogens have seven electrons in their outermost shells (ns2np5) and thus are one electron of the noble gas structure closest to them. Astatine seems to be the only radioactive element under this category. Both physical and chemical parameters show a consistent progression. The components in concern include chlorine, fluorine, bromine, astatine, and iodine.įurthermore, no other group of a contemporary periodic table has a connection to this degree. Halogens are members of group 17 of the periodic table (In Greek, the word ‘halo’ represents salt, while ‘genes’ means producing, and so collectively, it stands for salt-producing). Halogens are extremely reactive non-metals with properties strikingly similar to those of metals. Halogens are found in Group 17 (Halogens) of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
